 |
Causes
The main components of gallstones are cholesterol, another small portion is formed from calcium salts. Bile contains large amounts of cholesterol that usually remains as a liquid. If the bile becomes saturated because of cholesterol, so cholesterol can become insoluble and precipitate out to form bile.
Risk Factors
1. Gallstones are more common in women and risk factors are:
2. Elderly.
3. Overweight (obesity).
4. High-fat diet.
5. Heredity.
Pathophysiology
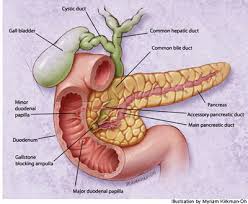
Most gallstones form in the gallbladder and the majority of stones in the bile ducts from the gallbladder. Gallstones can form in the bile duct if it has back-flow of bile due to the narrowing of the channel or after gallbladder removal.
Gallstones in the bile duct can lead to infection of the bile ducts great (cholangitis), infection of the pancreas (pancreatitis) or liver infection. If the bile duct is blocked, then the bacteria will grow and cause infection once in the channel. Bacteria can spread through the bloodstream and cause infection in other body parts.
The majority of gallstones in a long time does not cause symptoms, especially if the stones in the gallbladder settled. Sometimes large stones will gradually erode the gallbladder wall and into the small intestine or large intestine, causing intestinal obstruction (gallstone ileus).
What more often happens is out of gallstones and gallbladder into the bile ducts. Of the bile ducts, gallstones can enter the small intestine or remain in the bile ducts without causing interruption of bile flow and symptoms.
Symptoms and Signs
If gallstones suddenly clogged bile ducts, then the patient will feel pain. Pain tends to relapsing-remitting and pain known as colic. Occur slowly and reached its peak, then decreased gradually. The pain is sharp and relapsing-remitting, can last for hours. Location of pain varies, but most felt in the upper right abdomen and can spread to the right shoulder.
Patients often feel nausea and vomiting. If an infection with a blocked duct, it will have a fever, chills and jaundice (jaundice). Blockage is usually temporary and rarely infection.
Pain due to blockage of the channel can not be distinguished from pain due to gall bladder blockage. Permanent obstruction in the cystic duct causing inflammation of the gallbladder (acute cholecystitis). Gallstones that block the pancreatic duct causing inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), pain, jaundice and may also be infected.
Sometimes the pain of relapsing-remitting relapsed again after gallbladder removed, pain may be caused by gallstones in the main bile duct.
Complications
Complications that may be happening is:
* Bleeding
* Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
* Perforation or biliary tract infection.
In 2-6% of patients, shrinking the channel back and reappeared gallstones.
Prevention
Because the greatest composition of gallstones is cholesterol, should avoid foods high in cholesterol, which generally come from animal fats.
Management
If not found symptoms, then treatment is not necessary. Pain of relapsing-remitting be avoided or reduced by avoiding or reducing fatty foods.
Gallbladder stones
If the gall bladder stones cause repeated pain attacks have been carried out despite dietary changes, it is advisable to undergo gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy). Appointment of the gall bladder does not cause nutrient deficiency and after surgery is not necessary food restrictions.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy was introduced in 1990 and is currently about 90% done in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. The gallbladder is removed through a tube inserted through a small incision in the abdominal wall. This type of surgery has the following advantages:
* Reduce discomfort after surgery.
* Shortening the period of hospitalization.
Other techniques to remove gall bladder stones are:
* Solution with methyl-butyl-ether.
* Solving the sound waves (lithotrypsy).
* Dissolving with chronic bile acid treatment (kenodiol acid and acid ursodeoksikolik).
Bile duct stones
bile duct stones can cause serious problems, because it must be removed either surgically or through an abdominal procedure called Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). In ERCP, an endoscope is inserted through the mouth, esophagus, stomach and into the small intestine.
Radioopak contrast substance into the bile duct through a tube in the sphincter Oddi. In sfingterotomi, sphincter muscle to open a bit wide so that gallstones are blocking the channel will move to the small intestine. ERCP and sfingterotomi has been successfully performed on 90% of cases. Less than 4 of every 1,000 patients who died and 3-7% have complications, so that this procedure is safer than abdominal surgery. ERCP is usually effective only performed on patients bile duct stones are older, who had been appointed bladder bile.